How to Access Disc Drive on Windows 10
How to see all drives available on the computer
Updated: 07/06/2021 by Computer Hope
Note
This page provides information on how to determine which drives and drive letters your computer uses currently. It is not a list of all of the possible drive letters.
- Windows 10, and Windows 8.
- Microsoft Windows 7, Vista, XP and earlier.
- Windows 3.0, 3.1, and 3.11.
- MS-DOS and Windows command line.
- Apple macOS.
- Linux.
See drives in Windows 10 and Windows 8
If you're running Windows 10 or Windows 8, you can view all mounted drives in File Explorer. You can open File Explorer by pressing Windows key+E. In the left pane, select This PC, and all drives are shown on the right. The screenshot shows a typical view of This PC, with three mounted drives.

OS & Primary Software (C:)
In our first example, the C: and F: drives are hard drives, listed as primary and secondary. Most computers only have a C: drive. The hard drive is the primary location where all files are stored on your computer. To open the drive, double-click the drive.
Tip
In our example, the drives are labeled "Local Disk" and "New Volume." A hard drive can be labeled anything and may be different on your computer. For steps on changing the name of your drive, see: How to rename or label a disk drive.
DVD RW Drive (D:)
The D: drive in this example is the optical disc drive installed in the computer. In most situations, the disc drive will be the last drive letter. If a disc is in the drive, the contents of that disc are shown if you double-click the drive icon.
How to locate an External hard drive, memory card, or USB Drive on your computer
As long as an external hard drive, memory card, or USB drive is connected to the computer or on your network, they should appear in File Explorer. The external drive or USB will usually be labeled as "external hard drive", "USB Drive", or has the manufacturer of the drive listed in the drive name.
See available drives in Microsoft Windows 7 and earlier
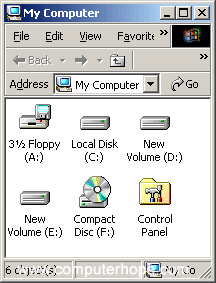
Microsoft Windows 7, Vista, XP, and earlier users can identify which drives Windows has detected by opening File Explorer and then My Computer, or pressing the Windows key+E shortcut key. The picture is an example of My Computer. As you can see in this example, three different drive types are listed.
Tip
In Windows 7 and earlier versions, you can access My Computer (Computer) by double-clicking the icon on the desktop. Or, open the Start menu, and select My Computer or Computer, depending on the version of Windows you're using.
3 1/2 Floppy (A:)
If the computer has a floppy disk drive, this drive is visible and usually set as the A: drive. If any floppy diskette is in the computer and the A: drive is opened, its contents are shown.
Local Disk (C:), New Volume (D:), and New Volume (E:)
Next, in our example, the C:, D:, and E: drives are hard drives or hard drive partitions on the computer. Most computers only have a C: drive. The hard drive is the primary location where all files are stored on your computer.
Tip
In our example, the drives are labeled "Local Disk" and "New Volume." A hard drive can be labeled anything and may be different on your computer. For steps on changing the name of your drive, see: How to rename or label a disk drive.
Compact Disc (F:)
Finally, the F: drive in this example is the optical disc drive installed in the computer. In most situations, the disc drive is the last drive letter. If a disc is in the drive, the contents of that disc are shown if you double-click the drive icon.
Tip
If the drive AutoPlays the disc, right-click the drive, and click Explore.
See drives in Windows 3.0, 3.1, and 3.11
Windows 3.0, 3.1, and 3.11 users can open drives through the Windows File Manager. In the File Manager, click the drive icons shown above the folder and files. By default, the C: drive will be open. If you want to move to the floppy disk drive, click the A: drive icon. If you're going to open the CD drive, click the D: CD-ROM drive icon.
See drives in MS-DOS and the Windows command line
Windows Vista, 7, 8, and 10 command line users
If you're using Windows Vista, 7, or 8, use the wmic command at the Windows command line to view available drives on the computer. At the prompt, type the following command.
wmic logicaldisk get name
Or, for a little more information, such as volume size, use this command:
wmic logicaldisk list brief
- See our wmic command page for further information and examples on this command.
Other Windows command line and MS-DOS version users
Unfortunately, there is no easy way to list all available drives on the computer through the MS-DOS prompt with one command. Below are different recommendations for viewing drives.
Change drive letter
Change the drive to an alternate drive letter to determine if a drive is available and ready if no error message is received.
- How to change drives in MS-DOS and Windows command line.
Fdisk
Running the fdisk command allows you to view how the hard drives are set up and configured on the computer. However, this command is only possible if you're running a version of MS-DOS or Windows that supports fdisk.
- See the fdisk command page for additional information about this command.
vol
Running the vol command on a drive displays the drive label and serial number if available. This command allows you to see what drives are detected.
- See the vol command page for additional information and help with this command.
See drives in the Apple macOS
From the menu bar, select Go, then select Computer, or press the Shift+Command+C keyboard shortcut.
You can also view all drives through the Finder application.
See drives in Linux
Linux users can use the fdisk command to see their partition and drive information.
How to Access Disc Drive on Windows 10
Source: https://www.computerhope.com/issues/ch000854.htm
0 Response to "How to Access Disc Drive on Windows 10"
Post a Comment